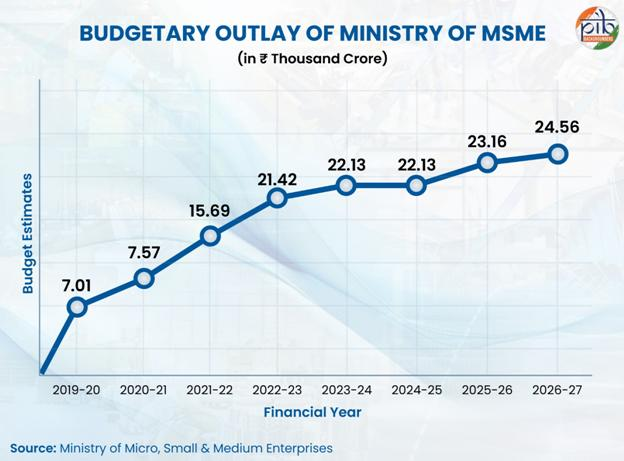
The Union Budget 2026–27 places Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) at the core of India’s economic growth strategy. With targeted financial, structural and policy reforms, the Budget outlines measures aimed at strengthening competitiveness, improving liquidity and expanding global integration of the MSME sector. The document highlights the sector’s contribution to manufacturing, exports and GDP, alongside new initiatives to support scale and innovation.
Union Budget 2026–27 Places MSMEs at the Centre of Growth
Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a significant role in India’s economic development by contributing to employment generation, manufacturing output and exports. With over 7.47 crore enterprises employing over 32.82 crore persons, MSMEs are the second-largest employer after agriculture. The Union Budget 2026–27 notes that MSMEs account for approximately 35.4% of manufacturing, 48.58% of exports and 31.1% of India’s GDP.

The Budget outlines three key Kartavyas: accelerating and sustaining economic growth; fulfilling people’s aspirations; and building capacities while ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Three-Pronged Approach to Develop MSME Champions
Under the first Kartavya, the Budget proposes a three-pronged strategy to help MSMEs grow as champions through equity support, liquidity enhancement and professional support.
1. Equity Support
A dedicated ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund has been announced to incentivise enterprises based on defined eligibility criteria and support the development of future champions.
Additionally, the Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund, established in 2021, will be augmented by ₹2,000 crore to continue providing risk capital to micro enterprises. As of 30 November 2025, the SRI Fund has supported 682 MSMEs through investments worth ₹15,442 crore.
2. Liquidity Support
More than ₹7 lakh crore has already been unlocked for MSMEs through the TReDS platform. To strengthen its impact, the Budget announces four key measures:
- Mandating TReDS as the settlement platform for all purchases from MSMEs by CPSEs.
- Introducing CGTMSE-backed credit guarantee support for invoice discounting on TReDS.
- Integrating GeM with TReDS to enable information-sharing with financiers on government MSME purchases.
- Introducing TReDS receivables as asset-backed securities to deepen the secondary market and improve liquidity.
TReDS is an electronic platform that facilitates financing and discounting of trade receivables of MSMEs through multiple financiers.
3. Professional Support
Professional institutions such as ICAI, ICSI and ICMAI will design short-term modular courses and tools to create a cadre of ‘Corporate Mitras’, particularly in Tier-II and Tier-III towns. These para-professionals will assist MSMEs in meeting compliance requirements at affordable costs.

Tax Proposal to Support Global Market Access
The Budget proposes removal of the existing ₹10 lakh per consignment value cap on courier exports. This measure is expected to ease cross-border B2C trade and support small businesses, artisans and start-ups in accessing global markets through e-commerce.
Technology-enabled tracking mechanisms will also be used to improve the handling of rejected and returned shipments.
Digital Transformation of MSMEs
Formalisation of MSMEs has accelerated, with over 7.30 crore enterprises registered on the Udyam Registration Portal and Udyam Assist Platform between 1 July 2020 and December 2025.
This includes:
- 4.37 crore registrations on the Udyam Portal
- 2.92 crore registrations on the Udyam Assist Platform
The Udyam Portal enables paperless, digital registration, while the Udyam Assist Platform brings Informal Micro Enterprises (IMEs) into the formal system for Priority Sector Lending benefits.
Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
PMEGP provides margin money subsidies on bank loans to micro-entrepreneurs. Since inception (FY 2008–09) until December 2025 (FY 2025–26), more than 10.71 lakh micro enterprises have been assisted with ₹29,249.43 crore in margin money subsidy, generating estimated employment for over 87 lakh persons.
MSME Champions Scheme
The MSME Champions Scheme supports enterprises through three components:
- MSME-Sustainable (ZED)
- MSME Competitive (LEAN)
- MSME-Innovative (Incubation, Design & IPR)
Under the scheme:
- 2,71,373 MSMEs registered under the MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification Scheme and 1,92,689 enterprises were certified.
- 32,077 MSMEs registered under the MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme and 31,987 MSMEs took the Lean pledge.
E-commerce and Supply Chain Initiatives
Expansion of the ONDC (Open Network for Digital Commerce) ecosystem and the TEAM (Trade Enablement and Marketing) initiative, which aims to onboard 5 lakh MSMEs, is intended to integrate enterprises into formal e-commerce supply chains and reduce transaction costs.
Online Dispute Resolution (ODR)
The MSE Scheme for Online Dispute Resolution (ODR) addresses delayed payments through a structured pre-adjudication mechanism under the MSMED Act, 2006. The ODR portal was launched on 27 June 2025, coinciding with MSME Day.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGSME)
The CGSME provides credit guarantees for collateral-free loans extended to MSEs.
Key highlights:
- Crossed 1 crore guarantees since inception in August 2000.
- 29.03 lakh guarantees approved worth ₹3.77 lakh crore between 1 January and 30 November 2025.
- Guarantee coverage ceiling increased from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore.
- A special provision for MSEs promoted by transgender entrepreneurs offers a 10% concession in guarantee fees and 85% guarantee coverage (effective 1 March 2025).
PM Vishwakarma Scheme
Launched in September 2023, the PM Vishwakarma Scheme provides support to artisans and craftspeople across 18 trades.
As of 1 December 2025:
- 30 lakh beneficiaries registered.
- 23.09 lakh beneficiaries trained.
- 20 lakh+ artisans receiving training and banking support.
- 7.7 lakh beneficiaries completed basic skill training in 2025.
- ₹2,257 crore sanctioned to 2.62 lakh beneficiaries as collateral-free loans in 2025.
- 6.7 lakh beneficiaries digitally enabled.
- 30,000+ beneficiaries onboarded on Government e-Marketplace.
Labour Reforms
Labour Codes aim to formalise employment, simplify compliance through digitisation, strengthen social security and improve workplace safety. The reforms reduce compliance burdens on MSMEs while maintaining worker safeguards.
Conclusion
Over time, the MSME sector has emerged as a major contributor to employment generation, rural industrialisation and balanced regional development. As ancillary partners to large industries, MSMEs strengthen the broader industrial ecosystem.
With policy support, financial measures and digital integration, MSMEs are positioned to enhance their role in manufacturing growth and global value chains under Union Budget 2026–27.
Source: PIB Research
